For any organization today, a data lake is the foundation of its IT infrastructure. This post will bring out the various intricacies of the SAP data lake, a modern data lake that brings a host of benefits to the table.
But before diving into the many aspects of the SAP data lake, it is necessary to understand the concept of data lakes per se.
A data lake is a storage service for all data that needs to be accessed by businesses at any time and processed for making analytical decisions. What distinguishes the present repositories like the SAP data lake from the traditional warehouses is that here, data can be stored in its native format – unstructured, semi-structured, or structured without processing and formatting. This saves a lot of time, costs, and complexities in data storage procedures.
This facet is what distinguishes a data warehouse from a data lake. In the former instance, only data that has been cleaned, processed, and structured can be stored while data in raw form can be stored in a data lake. In the current business environment, both can be present with one complementing and not substituting the other.
Further, unlike data warehouses, a data lake does not have one specific generic architecture and varies with businesses and use cases. Hence, the configuration of the SAP data lake is quite different from say, a Snowflake data lake even though both are in the category of data lakes.
The Launch of Cloud-based SAP HANA Data Lake

To strengthen its ecosystem of cloud-based offerings, SAP in April 2020 launched HANA Data Lake (HDL). The focus was to provide cost-effective storage alternatives to customers. The package included SAP HANA native storage extension and an in-built relational SAP data lake.
What does SAP data lake relational data lake signify? It means that the SAP IQ database is a cloud-based service with processing capabilities that are no less than the acknowledged leaders in this field like Microsoft Azure or Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service).
Among the cutting-edge features incorporated into the SAP data lake at launch is the 10x data compression ability that leads to a significant reduction in data storage cost. Also, the data lake can be easily incorporated either in the current HANA Cloud or in a fresh HANA Cloud instance.
In both options, storage space can be added at any time on demand. SAP data lake comes with the usual cloud-based data lake features like audit logging, data encryption, and tracking of data access.
The SAP data lake has a unique advantage for users. Businesses can keep their critical and most-used data (hot data) in memory for quick access and extraction for processing while moving less-used data (warm data) to the SAP HANA Native Storage Extension (NSE). For old data that might be used but rarely, the HANA Data Lake (IQ) ensures access at vastly reduced costs. This data tiering leads to proportionate pricing as the various segments have different storage costs as will be seen now.
The Unique Architecture of the SAP Data Lake
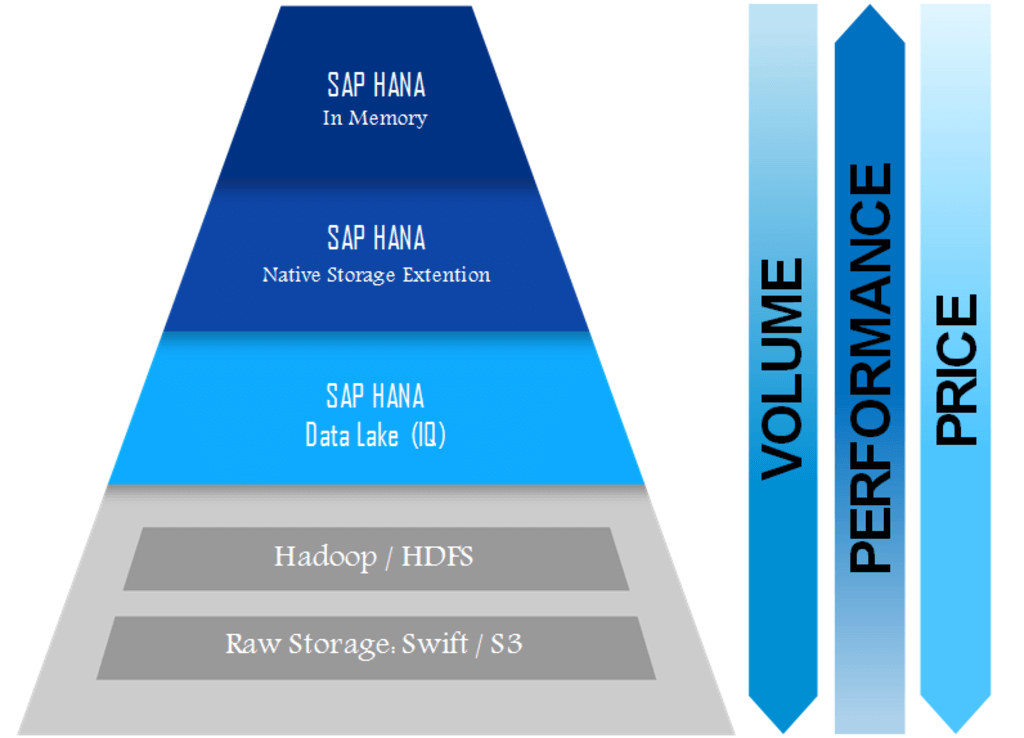
The unique architecture of the SAP data lake resembles a pyramid.
At the top of the structure, all data that is critical and of utmost importance to businesses and hence very valuable is stored. This data is frequently accessed and often wanted very urgently and is the hot data referred to above. Storage costs of this segment are naturally quite high given its status.
In the middle of the pyramid lies the data that in the past would be treated as cold storage and is usually voluminous. Thanks to the SAP data lake, access to this data is not difficult though not as quick as the top tier. The cost of this data storage is therefore lower.
At the bottom of the pyramid lies the rarely used data of organizations. Access to this data is slow but the trade-off here is that costs of storage are rock-bottom, canceling out the need for this data to be permanently removed.
Summing up, managing data through a reasonable life cycle, from hot data to warm to cold is ensured by the SAP data lake. This data tiering in a pyramid form keeps data storage costs affordable as prices depend solely on where data is stored based on the need for quick access without any flat and upfront charges.
Advanced Features and Benefits of the SAP HANA Data Lake

SAP HANA data lake offers several high-performing features, making it one of the preferred data lakes for most organizations around the world. Some of the key ones are as follows.
- Highly flexible and operated independently of HANA DB. Storage facilities can be scaled up to petabyte levels on demand, doing away with the need for investments in hardware and software whenever there is a spike in demand for more storage.
- Offers easy and seamless access to leading cloud service providers like Google Cloud Platform’s Cloud Storage and Amazon Web Service S3.
- Based on the latest and cutting-edge SAP technology.
- The SAP data lake is configured to automatically complement and be deployed with the HANA Cloud.
- The data lake is enabled for high-speed ingestion and has excellent data analyzing abilities.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) which is a financial estimate to help evaluate the direct and indirect storage costs is very low for the SAP data lake.
- The pyramid-like architecture ensures smooth and seamless quick data processing for analytics.
Given all these features and benefits organizations stand to gain a lot if the SAP data lake is deployed in their IT infrastructure.
In case you missed it!